Midterm 2 information/Learning goals
From UBCMATH WIKI
Contents |
Week 5
- Recognize that a given word problem is an optimization problem. (Something to this effect)
- Set up an optimization problem by finding the objective and constraint functions.
- Find an optimal value and show that it is optimal using appropriate methods.
Week 6
- Find the slope of the line of best fit, that passes through the origin, to a set of data by minimizing the sum of the squared residuals.
- Identify which line in a given set of lines best fits a given set of data.
Week 7
- Calculate the derivative of functions of the form
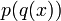 , where
, where 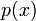 and
and 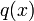 are either polynomials or rational functions.
are either polynomials or rational functions.
- Calculate the derivative of polynomial functions defined implicitly.
- Recognize that a given word problem is a related rates problem, translate the word problem into a mathematical problem, solve this mathematical problem and relate the answer back to the original word problem.
Week 8
- Use the properties of exponential and logarithmic functions to simplify, or rearrange expressions involving exponential and logarithmic functions.
- In particular, transform an expression involving general exponential and logarithmic functions to one involving the natural exponential and logarithm, $e$ and $\ln$.
- Calculate the derivative of $y=a^{f(x)}$, where $a$ is a constant and $f(x)$ is a function of $x$.
- Calculate the derivative of $y=\log_a(f(x))$, where $a$ is a constant and $f(x)$ is a function of $x$.
- Convert $(x,y)$ data to $(\ln(x),\ln(y))$ data.
- Find a line of best fit to $(\ln(x), \ln(y))$ data and transform this line to a power function in the $x-y$ plane.
Week 9
- Verify that a given function satisfies a given differential equation.
- Find a function that satisfies a given elementary differential equation.
- Find a function that describes the change in a quantity given information about that quantity's doubling or characteristic time.
- Solve for the constants in a general solution to a differential equation using the information given in an initial value problem.
- Solve for the doubling times and half lives in exponential growth/decay problems.